Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy shown to be effective in more than 1,000 studies. This short-term, structured treatment helps people identify goals and overcome obstacles. As claimed by the Beck Institute – and therapists everywhere – “CBT helps people get better and stay better.”
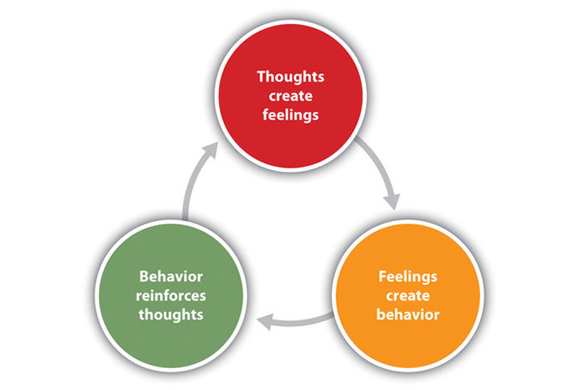
Cognitive therapy is different from other forms of psychotherapy. It is more oriented to problem solving. CBT introduces specific skills people can use throughout their lives. It teaches people to change negative thinking to alter emotions and behavior.
Cognitive Therapy History
Dr. Aaron Beck, an American psychiatrist, introduced cognitive behavioral therapy in the 1960’s. As a child, Beck suffered with fear and depression. The way he addressed his problems led to his therapeutic approach years later.
Beck noted a link between certain types of thinking and emotional problems. He called this thinking “automatic negative thoughts” … and developed a way to change it through cognitive therapy.
Early behavior therapies focused on associations, punishments, and reinforcements to change behavior. Beck’s approach addressed thought patterns and their effect on feelings and actions. Today, CBT is a first-line treatment for a wide range of mental health conditions.
Cognitive Therapy Uses
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a helpful tool for many different psychological problems. It is effective for anxiety, depression, eating disorders, marital problems, substance abuse, and more. It helps treat trauma effects such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
CBT is also helpful for people who do not have a mental health problem. It can teach anyone how to manage stress by changing thoughts and thinking patterns. Yet, it is about more than changing thoughts and thinking. Cognitive techniques help people overcome distressing thoughts and distorted beliefs so they can achieve their goals.
Cognitive therapy is a preferred modality among doctors and insurance companies. It is appropriate for all ages, and it can be effective in a short period of time – usually fewer than 20 sessions. Research suggests it is deliverable online or with in-person therapy sessions.
Cognitive Therapy Techniques
Cognitive therapy techniques are evidence-based treatment methods. They help people change thoughts, feelings, and behaviors to improve their lives. Current research informs the techniques. The list below represents the most common CBT procedures.
This technique helps people identify thought patterns responsible for negative moods and behavior. One practice is to track spontaneous thoughts to devise healthier thinking patterns. Cognitive restructuring is a common treatment for the trauma of PTSD.
In general, people avoid what they fear. This avoidance maintains feelings of fear, worry, and anxiety. Systematic exposure helps people approach fearful situations. In time, they can master their fears one-by-one.
Activity scheduling helps people increase helpful behaviors. By scheduling activities like walking and meditation, they are more likely to do them. This works especially well for less active people who experience depression or procrastination.
This technique works for people who have a hard time finishing a task – often due to feelings of overwhelm or the effects of trauma. The idea is to help people master an easy task that is similar in nature to a more difficult one. The rehearsed behavior can help the harder task feel more manageable.
Some problems stem from not having the right skills to achieve specific goals. Skills training solves this skills deficit. In cognitive behavior therapy, skills training occurs in several common areas. Assertiveness training, communication training, and social skills training are three examples.
Cognitivebehavioral therapy borrows mindfulness from Buddhism. The goal is to help people stop ruminating on negative things and focus on the present moment. A lot of new research focuses on mindfulness. This technique is on the cutting edge of modern psychotherapy.
Conclusion
Cognitive behavior therapy is an effective treatment choice for several mental health conditions. Anxiety, worry, depression, stress, and trauma are just a few examples. What’s more, CBT is appropriate for anyone from children and teens to adults.
“There is more on the surface than what our eyes can see,” said Dr. Aaron Beck. His therapy model is a good starting point for personal transformation. So, stop the negative thinking and “give yourself a chance,” Beck said.
